16 September 2025, NIICE Commentary 11748
Patrice Salzenstein
In 2025, Nepal finds itself at the crossroads of two diplomatic commemorations: its anniversary of cooperation with China, a key regional partner, and its 76th anniversary of relations with France. These two anniversaries illustrate Nepal’s strategy of balancing its immediate neighborhood relations with longer-term partnerships that transcend geography. The relationship between France and Nepal has been marked by continuity, solidarity, and shared values. While trade remains relatively small, cooperation has thrived in areas such as scientific research, culture, health, and climate policy. This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of Franco–Nepali collaboration, structured into political, cultural, economic, scientific, and multilateral dimensions. It is important to remind about the historical context of France–Nepal Relations. France and Nepal officially established diplomatic ties in 1949, only two years after Nepal joined the international community by opening its borders. Early cooperation included scientific missions in the Himalayas and anthropological studies. A milestone was reached in 1978 with the agreement between the French Commissariat à l’Énergie Atomique (CEA) and the Nepali Department of Mines and Geology. This cooperation on seismic monitoring has endured for nearly five decades, providing essential data for one of the world’s most earthquake-prone regions. In 2024, both countries celebrated 75 years of diplomatic relations, reaffirming their long-standing friendship.
Political and Diplomatic Exchanges
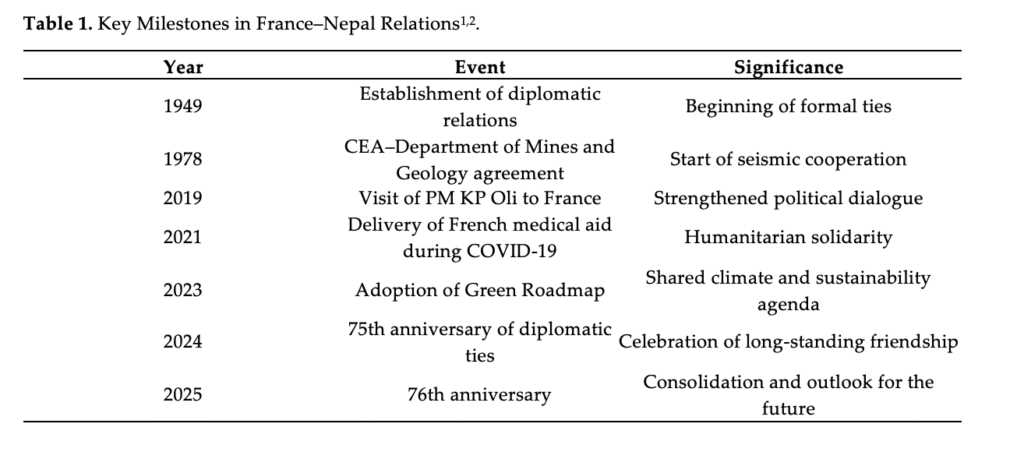
Political dialogue between France and Nepal has intensified over the past decade, marked by key high-level visits and sustained consultations: in March 2019, Nepal’s Minister of Telecommunications and Information Technology visited France, followed by Prime Minister KP Oli’s visit to Paris and Chamonix in June 2019, and from 2019 to 2025, a regular cycle of political consultations has been maintained, alternating between Paris and Kathmandu, with the most recent meeting held in June 2025 in Kathmandu. Table 1 summurizes this dialogue. France and Nepal share common diplomatic priorities regarding the defense of global commons, including biodiversity, freshwater resources, and glaciers. The adoption of the Franco–Nepali Green Roadmap in January 2023 confirmed this alignment. Humanitarian diplomacy also plays a role. During the COVID-19 pandemic, France delivered 7 tonnes of medical supplies in June 2021 and donated 1.58 million vaccine doses in July 2023 through the COVAX facility.
Cooperation between France and Nepal
Cooperation and economical relation are modest but some efforts are made for their development.
Economic Relations: Limited but Evolving
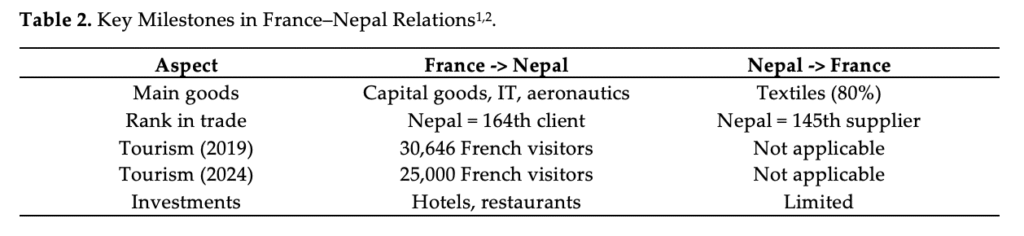
Trade between France and Nepal is modest but structurally complementary, with France exporting capital goods, IT equipment, and aeronautics, while Nepal exports primarily textiles, which account for 80% of its exports. According to the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Nepal ranks 145th as a supplier to France, contributing 0.00% of French imports, and 164th as a client, representing 0.00% of French exports. Tourism offers a more dynamic dimension to bilateral relations, with 30,646 French tourists visiting Nepal in 2019 and 25,000 in 2024, reflecting post-COVID recovery though still below pre-pandemic levels. French investment in Nepal is largely concentrated in the hospitality and restaurant sectors, underscoring the country’s significance as a tourism destination. Table 2 records the Key Milestones and Figure 1 represents the evolution of
trade of Goods between France and Nepal in 2018.
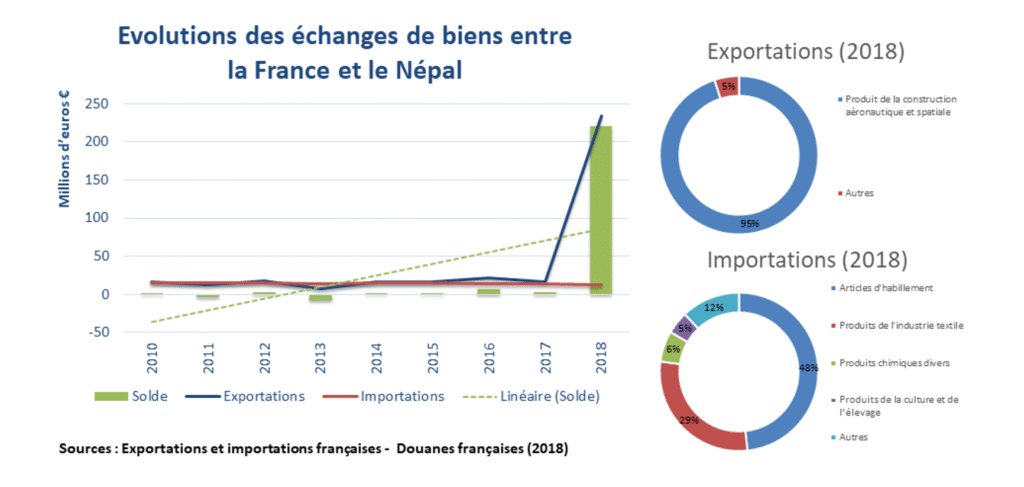
Figure 1. This Figure in French shows the evolution of trade of Goods between France and Nepal until 2018.
Cultural and Educational Cooperation
Cultural and educational cooperation forms a cornerstone of the bilateral relationship, with cultural diplomacy at its heart. The Alliance Française of Kathmandu serves as the primary hub for French cultural outreach, while the French International School of Kathmandu offers bilingual education, fostering early academic and linguistic exchange. Academic mobility is further supported by Campus France, whose research portal provides Nepali students with access to PhD opportunities in France. Collaborative initiatives also extend to heritage and linguistics, exemplified by the Collège de France’s digitization of a Nepalese manuscript, which combines preservation with broad digital accessibility.
Scientific Cooperation
Scientific collaboration is a cornerstone of Franco–Nepali relations, exemplified by the longstanding CEA–DASE partnership (1978–present), which monitors seismic activity through a network of sensors across Nepal. Joint initiatives extend to glaciology, biodiversity, and water resources, reflecting the pressing challenges of climate change, while the 2023 Green Roadmap further emphasizes sustainability, reinforcing scientific cooperation as a strategic pillar. This collaboration not only supports Nepal’s environmental and scientific development but also serves the global community, as Himalayan glaciers are vital indicators of worldwide climate trends.
France, Nepal, and the European Union
Since 1996, the EU–Nepal Cooperation Agreement has structured relations in areas such as human rights, trade, science, agriculture, and development. France, as an EU member state, complements this framework by offering targeted bilateral initiatives. The dual track (EU + France) enhances Nepal’s ability to engage internationally while maintaining national priorities.
Perspectives
Academic laboratories operate under a distinctive paradigm compared to National Metrology Institutes (NMIs) and industrial labs. While the latter typically focus on providing calibration services with legal or economic consequences (such as ensuring compliance with regulatory standards), academic labs primarily concentrate on advancing scientific understanding and technology. Their role is not to offer commercial calibration services but to explore the limits of measurement science and develop cutting-edge methodologies.
Comparative Perspectives: Nepal–China and Nepal–France
As illustrated in Table 3, Nepal–China relations, shaped by geographic proximity and extensive economic cooperation, focus primarily on infrastructure, connectivity, and projects under the Belt and Road Initiative, reflecting a pragmatic, neighborly engagement, whereas Nepal–France relations emphasize cultural exchange, scientific collaboration, sustainable development, and education, representing a partnership grounded in shared values and global priorities rather than geographic or economic asymmetry; together, these relationships illustrate Nepal’s foreign policy strategy of balancing regional pragmatism with broader global engagement.

Future Prospects for France–Nepal Relations
Future prospects for France–Nepal relations present several promising avenues for deepening cooperation. In the field of climate and environment, both countries can expand renewable energy projects, enhance water management, and support biodiversity conservation initiatives. Tourism offers opportunities to develop sustainable models that protect fragile Himalayan ecosystems while promoting economic growth. Education and research collaboration can be strengthened through scholarships, PhD programs, and joint digital heritage projects. In health, cooperation can extend beyond COVID-19 to broader medical and public health initiatives. Additionally, technology and innovation partnerships can flourish in areas such as aerospace, information technology, and environmental monitoring, creating a multifaceted framework for long-term bilateral engagement4,5.
Conclusion
The 76th anniversary of France–Nepal diplomatic relations highlights a partnership that is modest in trade but rich in cultural, scientific, and environmental cooperation. France has supported Nepal during crises, promoted knowledge through scientific research, and acted as a cultural bridge via education and the arts. As Nepal navigates its regional partnerships and global responsibilities, its cooperation with France illustrates how two distant nations can sustain a meaningful and forward-looking partnership, built not on asymmetry but on shared commitments to sustainability, cultural dialogue, and scientific progress. This collaboration serves as a model of how small states and middle powers can jointly address the global challenges of the 21st century.
Patrice Salzenstein is the Deputy Head of the Phononic & Microscopy team, at the Micro Nano Science & Systems department of CNRS UMR 6174 FEMTO-ST laboratory, with an interest in uncertainty estimations

